The Cause of the "Flower" Phenomenon
Due to the inability to effectively deionize and cause continuous arc discharge, the resistive heat of the arc precipitates a large amount of carbon to form carbon fine particles, and the molybdenum wire itself is also carbonized. Thickness of the workpiece (long discharge gap), low dielectric coefficient of water (poor recovery of insulation), and one of the three sources of the pulsed source with a delayed arc-extinguishing DC component (greater than 10 mA) are the basic conditions for the "flower filament" phenomenon. . The “impurities†brought into the discharge gap (or inherent in the workpiece) that affect the spark discharge are the cause of the “filament†phenomenon. "Filigree" is the same as the arc burn of spark discharge machining. Once the arc burn in the gap is formed, the workpiece and the electrode will be burned out of the pit and formed into charcoal particles. If the carbon fine particles are not cleaned, they cannot continue. Processing. Fine carbon pellets stick there, where arc burns will take place, and the area will become larger and larger, and there is absolutely no possibility of self-elimination. If the workpiece and the electrode are displaced, each new and the opposite arc will cause a new burn in the arc, one in two locations. The only way is for people to clean up, and the line cut is powerless.
The Occurrence and Development of "Filigree"
When the discharge gap is long, discharge of the erosion material is difficult, the ability to recover the insulation is poor, and the spark explosion is weak, “impurities†are easily generated, the resistance heat rapidly becomes arc burn, and the carbon fine particles are mixed together. During the movement of the wire, each pulse of energy is released through this point of arcing until the point of arcing is removed from the work piece, and insulation is only possible to recover, and new spark discharges may occur. Molybdenum wire burns at this point (ie dark spots) are formed. If the point where the arc burn just induced in the gap is still tenacious, it is very easy to repeat the arc discharge with the molybdenum wire point that is in contact with it, and the second burn carbonization (ie, black spot) point is formed again. So the distance between that point and the workpiece exit is often equal to the distance between the two dark spots. Since the first burn was carbonized, a carbonization point was left on the wire, and a series of charring spots were left in the workpiece gap. Fine carbon particles spread into the water at any time to enter the gap. They all became the inducement of “filigreeâ€. factor. It became a "cross-infection". At this time, no matter which silk, water, or work piece was changed, it would be useless to change everything. After a period of time, those predisposing factors for "cross-infection" have disappeared. The same conditions, or even the piece of material, can be cut.
The appearance and observation of "flower filament"
Due to arc discharge, short circuit, open circuit, and carbon pellets, the pulse source ammeter will swing significantly. Discharge sparks will appear red, yellow, and white. The black spots formed at the beginning are thickened by heat burning and carbonization, and pass through the gap and ablate several times and then become thinner. Heating and tensioning for a period of time also naturally thins the dark spots. Brittleness is caused by burning red and cooling and causing serious carbonization. Because the "flower filaments" formed in the silk tube are very easy to arrange regularly, many people try to find out the laws. The result is not the same as the circumference of the package, the circumference of the guide wheel, and the distance between the conductive block and the user. If there is regularity, it is the distance from the point of burn to the exit of the workpiece.
"Filament" Solution and Analysis
Once the "filament" phenomenon has occurred, we must start with the three elements of the cause. First of all, to confirm the quality of the pulse generator, as long as there is no DC component that prevents arcing, it usually does not cause thread breakage. Second, we must pay attention to water, dirt, rare earth, and less effective components, certainly not; containing a certain amount of salt, alkali and other components that hinder dielectric insulation is even more difficult. Once again, we must pay attention to the fact that thin materials are all good. Even if there is an incentive to pull an arc burn, the exchange of water is quick, and the elimination of impurities and impurities is easy to eliminate. Thick, the incentive to pull the arc burn is very easy to produce and extremely difficult to discharge. Especially with oxidation black, forged sandwich, raw materials quenched without forging and tempering, resulting in a high probability of "flower filaments."
After the "filigree" material, silk, and water have only one of them, the possibility of "filigree" is still very high.
If you can't help but can only cut this piece of material, then completely replace the wire, change the water, clean the machine tool; material sandwich, quenching has no way, at least remove the surface oxide black skin clean; avoid the cut that has been cut. With large pulses, large pulse widths, small currents, and high voltages, when the stability of the process is only slow, the current can be gradually increased, but still limited to 2.5A.
1. Naipu Submersible sewage Slurry Pump introduction
NP-WQ series of submersible sewage pumps are designed with varies of installation experience and improved in water flow stream line, motor cooling system, Protections, control and sealing to suit for multipurpose applications and installations.
Typical Applications---
Municipals sewage installations
Constructions
Industrial waste water
Waste content solid and fibers
River and drain water
2. NP-WQ Submersible Sewage Slurry Pump strcuture drawing(mini type):
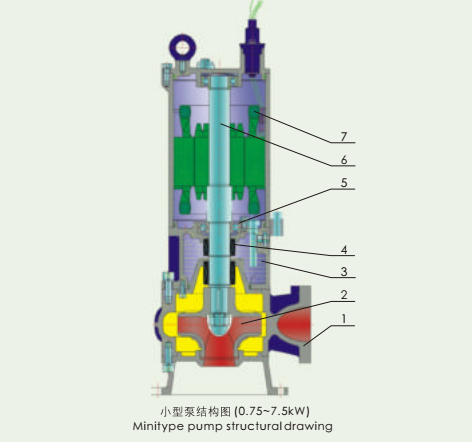
Main parts in the drawing:
1. pump casing 2. impeller 3.oil chamber 4.Bearing seal 5.bearing 6.pump motor shaft 7motor.
Medium type submersible sewage slurry pump strcuture drwaing:
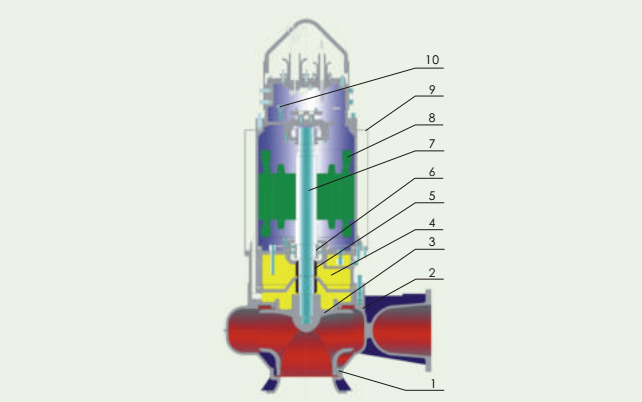
Main parts in the drawing:
1. wear ring 2. pump casing 3. impeller 4.oil chamber 5.Bearing seal 6.bearing 7.pump motor shaft 8.motor 9.cooling water jacket 10.inspect equipment
Submersible Sewage Slurry Pump
Submersible Pump, Submersible Sewage Pump, Submersible Slurry Pump, Vertical Submersible Slurry Pump
Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com